Understanding of Digital Public Infrastructure & India Stack.
Dive into a detailed and engaging overview of India's digital frameworks: India Stack, Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI), and Health Stack.
This piece I had co-authored with
. We have tried penning down to help you better understand DPI, India Stack and it’s significance to India Growth.
India is is currently undergoing an unparalleled digital revolution and phenomenal growth, which might have taken five decades under traditional West way, but has been able to achieve in under a decade, largely due to the implementation of Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI). This what Rahul Matthan says in his book as THE THIRD WAY - INDIA WAY!
The government’s initiatives like Digital India, JAM trinity (UPI, Aadhar, Mobile), India Stack and Digital Public Infrastructure have played a pivotal role in empowering billions of citizens by fostering financial inclusion and delivering public services through digital platforms.
These initiatives are the witnesses of significant transformations across sectors, from digital payments and e-commerce to government services and credit enablement, all driven by widespread internet access and cutting-edge technology.
Okay, so what is India Stack and DPI? What is the difference between these two?
Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI)
Much like how governments invest in building physical infrastructure such as roads, railways, and airports to benefit citizens, the Indian government took a visionary step by developing Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) or Digital Public Intelligence is what being called by the ‘Chief Technology Officer of India” Nandan Nilekani. NN spearheaded the entire DPI and India Stack initiatives, hence he’s called as CTO of India. This new approach leverages technology in a transformative way to tackle societal challenges, offering innovative solutions that enhance access to services, promote financial inclusion, and empower citizens across the country.
DPI provides the theoretical and structural framework, applicable worldwide, for building digital public systems, while India Stack is a concrete implementation of these principles, tailored to address specific national challenges and goals in India. DPI is the larger set and India Stack is the subset to it. DPI is being enabled by the Beckn Protocol, which is permission distributed ledger technology. Just that India Stack enables Financial Inclusion in India and there are other DPI which would be discussed in sometime that would be domain specific - Health Stack, Investing Stack, Agri Stack, Unified Energy Interface, etc.
India Stack: Population Scale Solution
India Stack is nothing but government-supported Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) that is written using set of open application programming interfaces (APIs). This digital framework is designed to be interoperable, enabling private companies to create applications that seamlessly integrate with public services, providing consumers with effortless access to a range of services from identity to payments to credit enablement applications and what not.
India Stack has radically transformed India's digital landscape by enabling innovative,
Paper-less
Presence-less,
Cash-less and
Consent layer
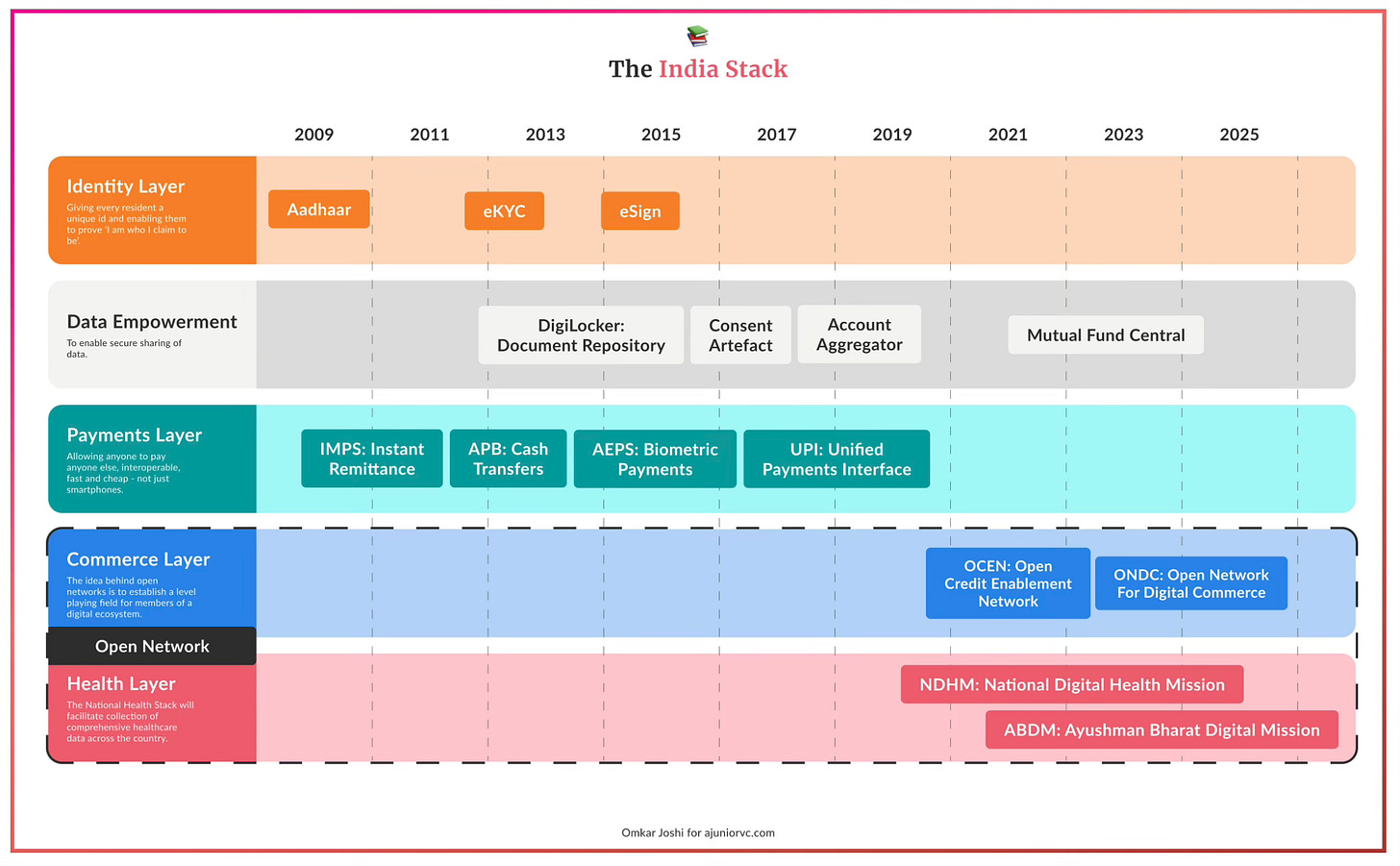
Core Layers of India Stack
India Stack comprises several foundational layers, each serving distinct functions within the digital infrastructure. Each layer would be discussed in detail as a separate piece. For now, on higher level:
Identity Layer - Presence-less
Aadhaar: Provides a 12-digit unique ID linked to individuals' biometric data, serving as a universal identity mechanism. This is base for any layer built on top of it.
eKYC and eSign: Facilitate electronic authentication and digital signing using Aadhaar, streamlining customer onboarding and document processing.
Payments Layer - Cash-less
Unified Payments Interface (UPI): A real-time payment system that simplifies transactions across different banks and financial institutions.
Aadhaar Enabled Payment System (AePS) and Bharat Bill Payment System (BBPS): Enable inclusive financial services by allowing transactions and bill payments through biometric authentication .
Data Layer - Paper-less & Consent
DigiLocker: Offers a secure digital locker for storing and sharing verified electronic documents.
Account Aggregator System: Enables consent-based sharing of financial data, promoting financial inclusion and simplifying lending and investment processes .
(Above graphic work is done by Omkar from ajuniorvc - Great work!)
Let’s go deep with core layers of India Stack.
Presence-less Layer:
So, we all know what is the scene with Aadhar 1.0. Now, recently at GFF 2024, Aadhaar 2.0 was introduced and it is like the next big upgrade to India’s digital identity system. Imagine Aadhaar got a fresh, shiny update with six new features to make everything from verifying your identity to logging into apps way easier and more secure. Here’s what’s cool about it:
1. Face Authentication (Yes, it's been around for 6 years!)
It’s pretty straightforward — instead of using your fingerprint all the time, you can just use your face to authenticate. This works especially well if your fingerprints aren't that clear, like for people in manual labor or older adults. Face recognition has grown a lot and is super stable now!
2. Verifiable Credentials
You know how you share data from your phone to someone else’s using NFC or Bluetooth? Now imagine doing that for your personal credentials but safely! Aadhaar 2.0 lets you share data via deep links, NFC, or BLE(Bluetooth Low Energy), using a technology called Zero-Knowledge Proofs. This means you can prove your info is legit without spilling all your personal details — kind of like showing just enough to get the job done.
3. Contactless Biometrics
No more touching fingerprint scanners! You can now authenticate yourself biometrically, completely contactless. And guess what? This feature builds heavily on face authentication, so just look at your phone and you’re good to go. It's hygienic and super convenient, especially in a post-pandemic world. Definitely a worthy alternative to OTP based authentication.
4. Aadhaar Status Check for Businesses
Businesses can now quickly check if your eKYC (electronic Know Your Customer) is still valid. For example, banks can see if your Aadhaar-linked KYC is up-to-date without asking you to re-submit documents. This streamlines processes for everyone.
5. Login with Aadhaar
This is cool — you can now log in to third-party apps using Aadhaar, much like you use Google or Facebook to log in to different apps. It’s built on OAuth 2.0, which is a secure protocol, so no need to remember a million passwords!
6. Innovation Sandbox
Lastly, this one's for all the tech nerds out there. The Innovation Sandbox lets developers and startups play around with Aadhaar’s features, testing new ideas and building innovative apps using Aadhaar’s infrastructure. It's like a playground for innovation where you can experiment before taking your app live.
Why does this matter?
Imagine how much easier life gets with all these features. You can log in quickly, share your data securely, and even use your face to verify yourself without touching anything! Plus, businesses benefit by cutting down on paperwork and validation time. Aadhaar 2.0 makes everything more seamless, secure, and ready for the future.
Cash-less Layer:
India represents nearly half of the world's digital payments, holding a 48.5% share of global real-time payment volumes, according to a report released by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) on August 5, 2024.
For the month of September 2024, UPI transactions remained above ₹20 lakh crore in value for the fifth consecutive month. The average daily transactions reached ₹68,800 crore, up from ₹66,475 crore in August.
India’s payment system was already strong before 2015, with platforms like IMPS, NEFT, and RTGS in place. Even though IMPS allowed real-time transfers, it wasn’t the go-to choice for smaller, frequent transactions. Then RBI thought of building UPI on top of IMPS rail which eventually has become an everyday thing.
I know we’ve all heard a lot about UPI, but as a Product Manager, I can’t help but highlight some of the impressive products that NPCI has developed around UPI. Here’s a quick rundown of what they’ve built:
UPI Lite: This one’s for those small, everyday transactions where you don’t need to enter a PIN. It’s super convenient for quick payments.
UPI Tap & Pay: Instead of the usual scanning of a QR code, you can now just tap it. It uses NFC technology, making the transaction even smoother. No more lining up the camera perfectly!
UPI Autopay: Perfect for recurring payments, like subscriptions. You set it up once, and it handles all those monthly payments without you needing to do anything.
UPI Circle: This is super handy for shared payments. It lets more than one person use a UPI account by assigning payment permissions. Think of it as a tiered delegation system for payments. I have previous written about it in detail - Check here.
UPI Block Mechanism: This is pretty smart—think of it as an escrow for IPOs. You block the funds when you apply, and if you get the allocation, the money transfers. If not, the funds are instantly unblocked for you to use again.
UPI 123: Facilitation to make payments for the non-smartphones or feature phones.
Hello UPI: Voice enabled payment systems for the people who are convient in sending money through voice.
UPI for NRIs: Even NRI’s can start using UPI using their NRI numbers.
UPI International: Funds can be transferred cross-borders using UPI.
These are just a few examples, but it shows how NPCI has really thought about user convenience and flexibility with UPI.
NPCI, the father of UPI had been working with 20+ countries through its international wing called NPCI International Payments Limited. Several countries have adopted UPI in various forms, including France, UAE, Saudi Arabia, Bahrain, Singapore, Maldives, Bhutan, and Oman. The USA started off late with their own real-time payment system after seeing the rapid adoption and the use case it served to India.
Paper-less Layer and Consent Layer:
The DigiLocker platform, introduced in 2015, functions as an application that securely stores users' digital records. This app facilitates various activities such as passport applications, academic marksheet reviews, and identity verification during travel. It is an integral part of the Indian government's initiative to become a digital wallet where they can access, authenticate, and manage crucial documents easily. As of early May, DigiLocker boasts over 270 million registered users and has facilitated the retrieval of nearly 6.7 billion documents, including Aadhaar cards, insurance policies, PAN records, and driving licenses.
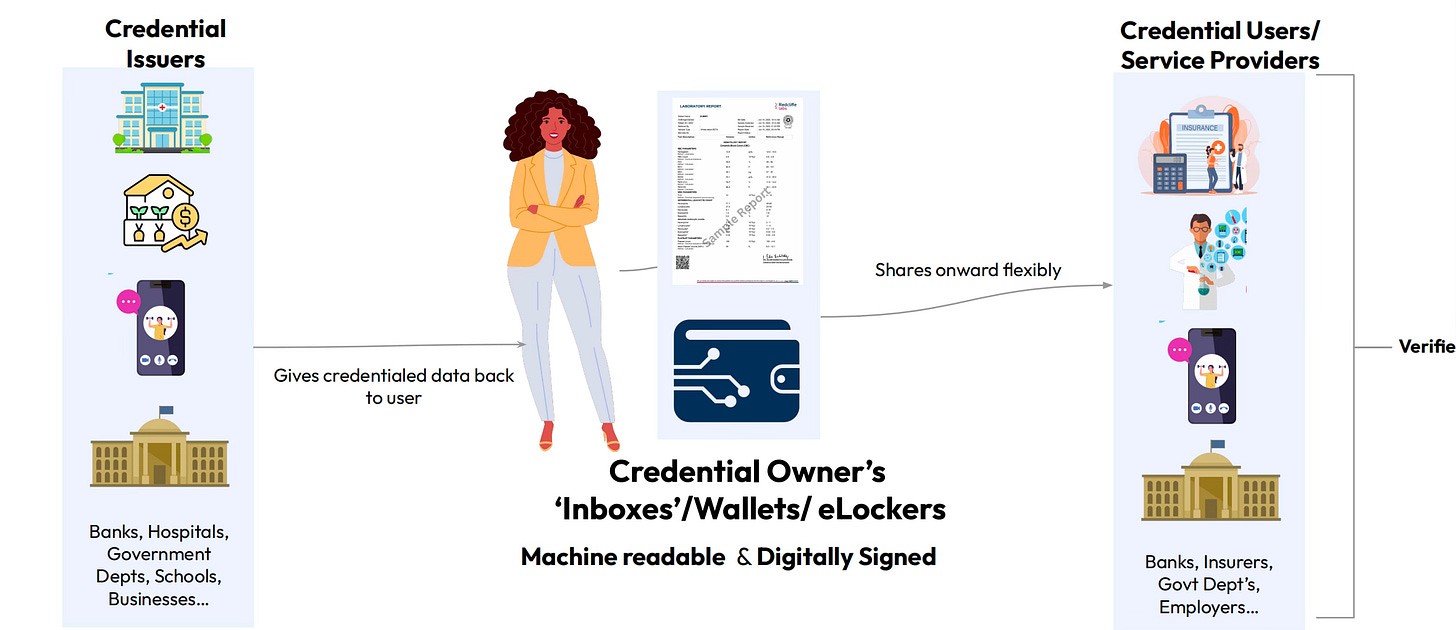
Here comes by favourite part of the piece, Account Aggregator.
The Account Aggregator (AA) marks the initial application of a "consent based" as outlined in the Data Empowerment and Protection Architecture (DEPA) Act. Essentially, a consent artefact is a mechanism that records and retains the permissions granted by a user. The AA is pivotal as it preserves the history of user consents for sharing financial data, with plans to extend similar models to other sectors like healthcare through Electronic Health Records (EHR).
(Source: Presentation from Dr. Pramod Varma on DPI)
Regulated by the RBI, the AA acts as an intermediary, facilitating the transfer of financial details from individuals to Financial Information Users (FIU) such as loan providers, expense management services, or wealth management applications. This information is sourced from Financial Institutions where the user holds accounts, like banks, mutual funds, depositories, or brokerage accounts. Importantly, the AA only retains the user's consent and does not access or "see" the actual user data.
The implementation of the AA system is poised to significantly reduce the costs associated with processing and monitoring loans. Accurate and timely updates from Financial Information Providers (FIPs), authorized by user consent, can enhance the efficiency of loan disbursement processes. Such improvements could make it economically feasible for lenders to offer smaller loan amounts, similarly to how UPI facilitated micro-payments, AAs might revolutionize micro-loans.
Traditionally, high processing costs have made only larger loan amounts financially viable for banks, leaving a substantial portion of the population without access to financial services. However, the AA model reduces these barriers, potentially broadening financial inclusion.
Here’s an example where CRED has partnered with Finvu, an AA provider. The AA in CRED enables you to link all your bank accounts into one single app to see your portfolio. And the use case can also be extended for a small flower merchant to better understand daily income flow and basis that credit enablement can be provisioned by the FIP to FIU (in this case small flower merchant).
Health Stack:
Imagine a healthcare system where every aspect of your medical information is at your fingertips—secure, accessible, and seamlessly integrated. That's the vision behind the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM), launched on September 27, 2021. This groundbreaking initiative is reshaping how healthcare is delivered across India, making it more accessible, efficient, and transparent by harnessing the power of digital technology.
The Birth of ABDM
The story of ABDM begins with India's National Health Policy of 2017, which set the stage for a health system built around accessibility, wellness, and digital integration. Building on this vision, the National Health Stack in 2018 and the National Digital Health Blueprint in 2019 laid the groundwork for a digital-first approach in healthcare, setting the stage for ABDM's impactful journey.
The Core Components of ABDM
ABDM isn't just a policy; it's a practical application of cutting-edge technology designed to serve everyone from city dwellers to rural populations:
Unique Health Identifier (ABHA ID): Every Indian now has the opportunity to own a unique health ID, simplifying the way health records are stored and managed.
Healthcare Professionals Registry (HPR): This comprehensive directory lists healthcare providers across both modern and traditional practices, ensuring they're woven into the fabric of India’s healthcare ecosystem.
Health Facility Registries (HFR): Including every health facility in the country, from the largest hospitals to local clinics and pharmacies, ensuring all are part of the national network.
Health Information Exchange and Consent Manager (HIE-CM): This tool puts power back into the hands of the people, allowing everyone to control who sees their health records and when.
Unified Health Interface (UHI): This interface makes it easier than ever to discover and access health services, streamlining patient experience.
National Health Claims Exchange (HCX): Simplifying the insurance claims process to make it faster and more user-friendly.
In just a few short years, ABDM has made incredible strides:
Expansive Reach: Over 67 crore Ayushman Bharat Health Accounts have been created, opening doors to secure health data management.
Widespread Connectivity: More than 42 crore health records are now connected to these accounts, with 3.3 lakh health facilities and nearly 4.7 lakh healthcare professionals integrated into the system.
Enhanced Interoperability: Both private and public health entities have been brought into the fold, significantly improving the ability to share and utilize information.
ABDM is continually innovating to enhance digital health adoption:
Scan and Share: A simple QR code has revolutionized how patients register at outpatient departments, slashing wait times and boosting data precision.
Digital Health Incentive Scheme: With attractive incentives, this scheme motivates healthcare providers to adopt digital systems.
End-to-End Adoption Pilot: Select facilities are being transformed into fully digital institutions, serving as models for others across the country.
Strategic partnerships are at the core of ABDM’s strategy:
Collaboration with IIT Kanpur: Focused on developing AI-driven solutions for health.
Partnership with Maharashtra University of Health Sciences: Integrating digital health into medical education to prepare the next generation of healthcare professionals.
The Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission stands as a beacon of India's commitment to revolutionizing healthcare through digital transformation. It’s not just improving healthcare delivery; it's empowering citizens, ensuring that everyone has access to efficient, transparent, and responsive healthcare services. As ABDM continues to grow, it promises to further revolutionize the healthcare landscape, making a healthier India a tangible reality for all.
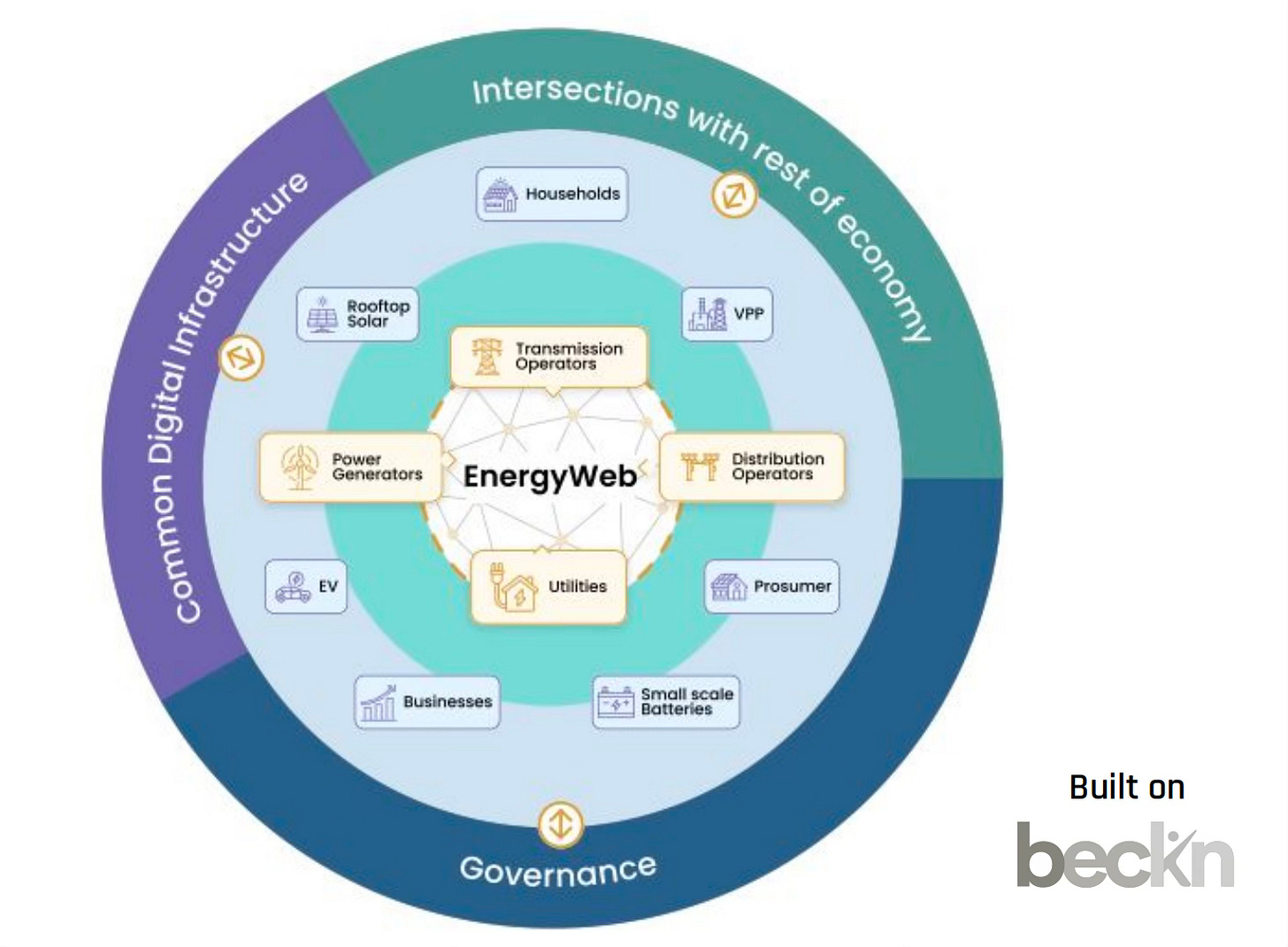
Unified Energy Interface: Early Stage
The Unified Energy Interface (UEI) is an exciting initiative launched by a consortium of 20 leading energy companies, including names like ChargeZone, Pulse Energy, Kazam, Sheru, Trinity, and Turbo. They've come together to develop an open energy network that makes transactions for electric vehicle (EV) charging completely seamless across different providers.
This innovative network is all about boosting the efficiency of energy transactions and is poised for significant expansion as more business-to-consumer (B2C) apps integrate with the platform. So far, the UEI has impressively handled 1.4GWh of energy transactions, and it's projected to see a staggering 100-fold increase as it grows.
One of the standout features of the UEI is its support for peer-to-peer trading of green electricity. This means you can directly buy and sell green electricity with others on the network, marking a major leap forward in fostering a sustainable green energy revolution.
For everyday consumers, the UEI offers a massive convenience boost. Whether you're charging your EV at a station run by any of the member companies, the process is standardized—you won't need a pile of different access cards or numerous accounts. Just one unified system lets you discover, pay for, and start charging without any hassle. This simplicity not only makes electric vehicle charging easier but also stirs up healthy competition and innovation among charging station operators, benefiting everyone involved.
If you have reached till here, then Thank you so much for reading this all through. There’s a lot to India’s DPI and its impact. In my next piece, I will cover Travel Stack, Investing Stack, Agri Stack, OCEN in detail and others.
I had co-authored with
, my dear friend for this piece. Took tremendous efforts and hours of research and comprehension of books to better understand India Stack and DPI. If you really liked our work, support our work and look forward to your constructive feedback!







Great piece @Kishoregoutham. Way to go. 👏